Irrigation
on autopilot
Lumo’s Irrigation Automation Solution is Purpose Built for Growers
We completely reconfigured the way growers automate their irrigation. No more controllers or base stations. No more trenching for wires. No more wondering whether a scheduled irrigation actually happened
All-in-one
Irrigation Automation

Hardware - Lumo One
The only smart irrigation valve with built-in communications and flow monitoring.
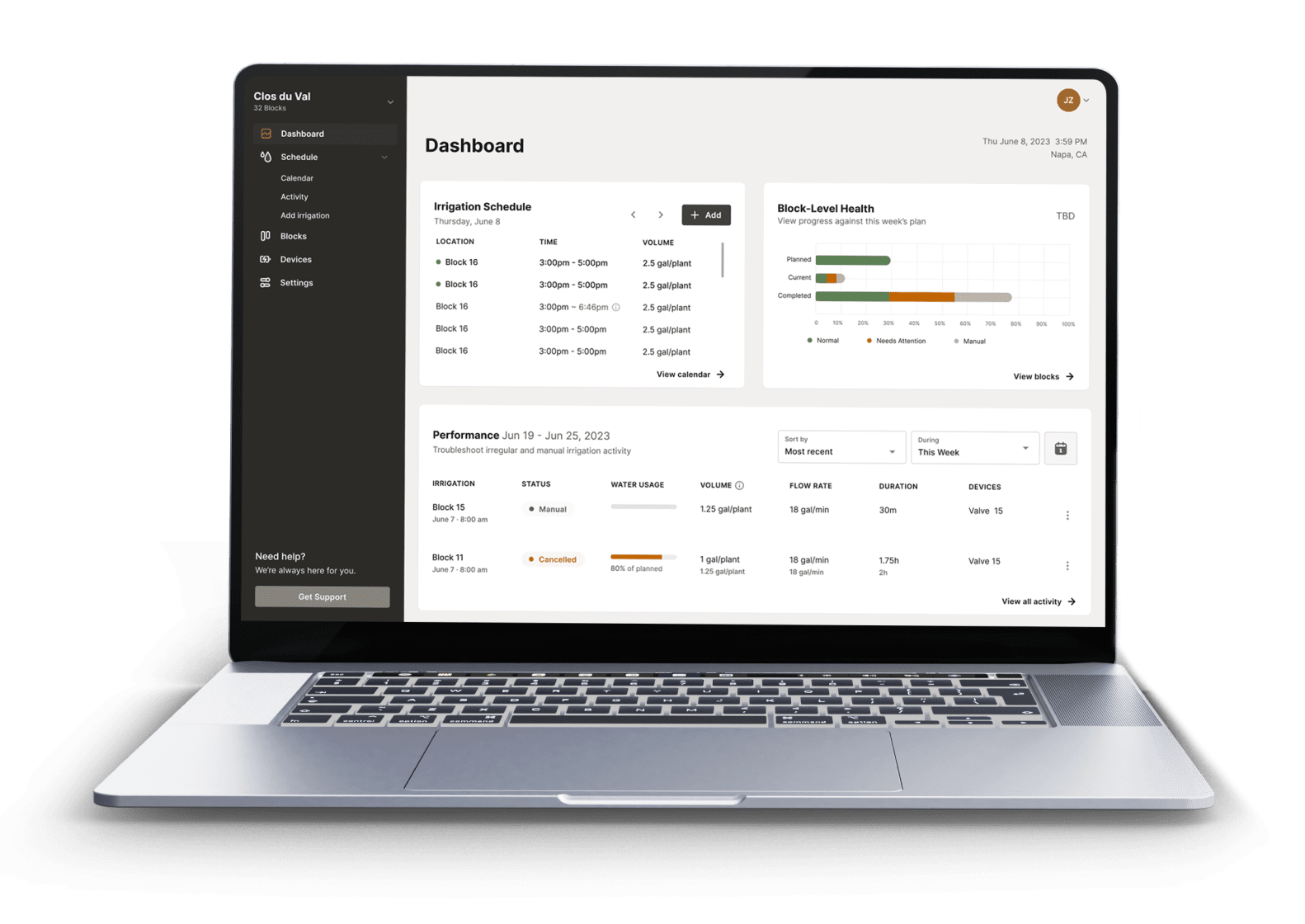
Software - The Ops Center
Irrigation management software that provides complete visibility and control over your irrigations.

Service
Support and service comes standard and is available on-site and on-line
How Irrigation
Automation Works
- 1. Install Lumo One valves in your irrigation blocks/zones. Done by you or our Field Team.
- 2. Log in to The Ops Center to create or modify your irrigation schedule.
- 3. Lumo automatically runs irrigations and monitors for leaks or abnormalities.
- 4. Audit and optimize your irrigation operations with data and reporting.
Irrigation Automation
Benefits
Eliminate Costs
by automating up to 90% of your current irrigation labor.
Monitor Your Irrigations
in real-time with Lumo’s irrigation management software.
Deliver the Exact Amount of Water
by specifying a target volume by block or zone.
Backed by Your Local Lumo Support Team
to ensure your irrigations perform flawlessly.

DIG DEEPER intoIrrigation Automation
Irrigation automation in agriculture refers to the use of technology to control and manage irrigation systems without requiring manual intervention. This approach leverages sensors, controllers, and software to optimize water delivery based on real-time data, improving efficiency, conserving water, and enhancing crop health.
Key Components of Automated Irrigation Systems:
Sensors:
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Monitor soil water content to determine when irrigation is necessary.
- Weather Sensors: Measure rainfall, temperature, humidity, and wind to adjust irrigation schedules.
- Flow Meters: Track water usage to detect leaks or inefficiencies.
Controllers:
- Centralized or remote devices that activate or deactivate irrigation based on data from sensors.
- They allow programming of schedules or dynamic adjustment based on environmental conditions.
Valves and Pumps:
- Operated automatically to deliver water to specific zones or crops as needed.
Communication Systems:
- Technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or IoT enable remote monitoring and control of the system.
- Systems can be integrated with smartphones or computers for easy management.
Software and Data Analytics:
- Platforms analyze data from sensors to optimize irrigation schedules and water usage.
- Some systems use AI to predict crop water requirements and provide recommendations.
Benefits of Irrigation Automation:
- Water Efficiency: Reduces waste by irrigating only when and where needed.
- Labor Savings: Minimizes manual effort in monitoring and operating irrigation systems.
- Increased Yields: Ensures crops receive consistent and optimal water supply.
- Energy Conservation: Efficient water usage reduces the energy required for pumping.
- Scalability: Easily adapts to both small-scale farms and large agricultural operations.
- Environmental Benefits: Limits overwatering, runoff, and soil erosion.
Types of Automation:
- Semi-Automatic Systems: Require some manual inputs, like turning on the system, but automate the irrigation process afterward.
- Fully Automatic Systems: Operate entirely on programmed schedules or sensor inputs without manual intervention.
- Smart Systems: Integrate AI and IoT technologies for real-time, data-driven irrigation decisions.
Applications in Agriculture:
- Greenhouses with precise water needs.
- Orchards and vineyards requiring zone-specific irrigation.
- Large-scale farms for efficient water management across extensive fields.
- Drought-prone areas to maximize limited water resources.
Automated irrigation represents a critical step toward sustainable and precision agriculture, helping farmers achieve better productivity with fewer resources.
When choosing an irrigation automation system, it is important to consider factors such as the type of crops being grown, the soil type and texture, the climate and weather patterns in the area, and the availability of water resources. It is also important to consider the cost of the system and its installation and maintenance requirements.
Irrigation automation can help conserve water by delivering water only when and where it is needed, reducing waste from overwatering or inefficient delivery. By using sensors and other technology to monitor soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and other factors, irrigation systems can optimize water delivery and reduce overall water use.
Common challenges associated with irrigation automation include system complexity, sensor and equipment maintenance, and data management and analysis. Ensuring that sensors and controllers are properly calibrated and maintained is important to ensure accurate water delivery, and managing data from multiple sources can also be challenging.
Learn more - Book a demo with our team