Farm Irrigation Technology
Modern and Intuitive Farm Irrigation Technology
Lumo’s farm irrigation technology uses cloud-managed software to power a network of smart water valves, making irrigation automation easy, data driven, and accountable
All-in-one Farm Irrigation SOlution

Hardware - Lumo One
The only smart irrigation valve with built-in communications and flow monitoring.
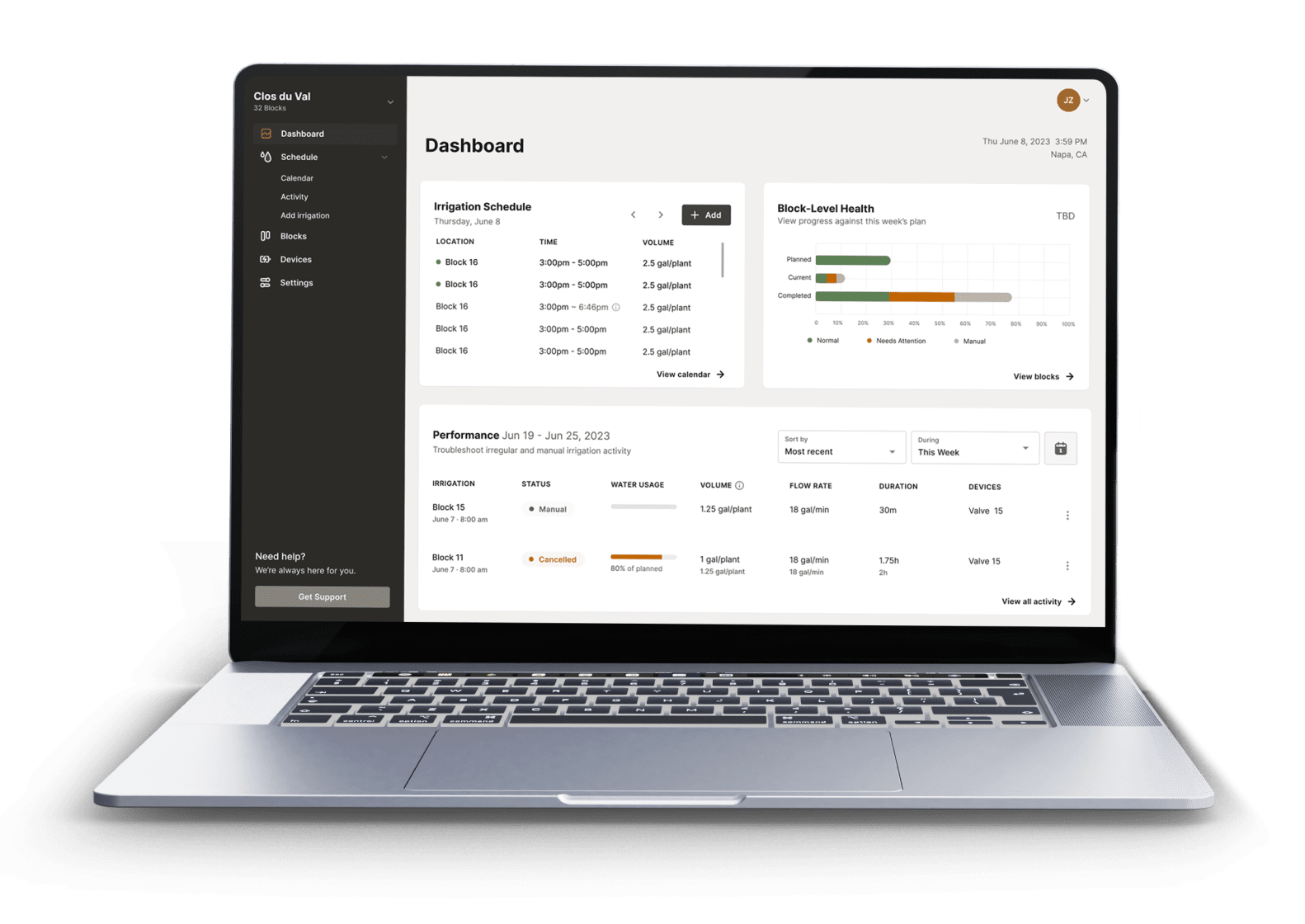
Software - The Ops Center
Irrigation management software that provides complete visibility and control over your irrigations.

Service
Support and service comes standard and is available on-site and on-line
How Farm Irrigation With Lumo Works
- 1. Install Lumo One valves in your irrigation blocks/zones. Done by you or our Field Team.
- 2. Log in to The Ops Center to create or modify your irrigation schedule.
- 3. Lumo automatically runs irrigations and monitors for leaks or abnormalities.
- 4. Audit and optimize your irrigation operations with data and reporting.
Farm Irrigation Benefits
Eliminate Costs
by automating up to 90% of your current irrigation labor.
Monitor Your Irrigations
in real-time with Lumo’s irrigation management software.
Deliver the Exact Amount of Water
by specifying a target volume by block or zone.
Backed by Your Local Lumo Support Team
to ensure your irrigations perform flawlessly.

DIG DEEPER Into Farm Irrigation
Farm irrigation is the process of applying water to crops to help them grow and thrive. It can be done through various methods, such as surface irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, and more.
Irrigation is important in farming because it provides crops with the necessary water they need to grow and thrive. Without irrigation, crops would not receive enough water, which could lead to poor growth and lower yields.
The different types of irrigation systems include surface irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, center pivot irrigation, and more.
Some factors that affect irrigation on your farm include soil type, crop type, climate, water availability, and irrigation system type and efficiency.
Farm irrigation best practices aim to maximize water efficiency, crop yields, and environmental sustainability. Here are some key practices:
1. Use Efficient Irrigation Systems
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Sprinkler Systems: Use in areas where uniform water distribution is necessary.
- Subsurface Irrigation: Ideal for areas prone to water scarcity, reducing evaporation losses further.
2. Monitor Soil Moisture
- Use soil moisture sensors to determine when and how much to irrigate.
- Avoid overwatering, which can lead to waterlogging and nutrient leaching.
3. Schedule Irrigation Wisely
- Irrigate early in the morning or late evening to reduce evaporation.
- Align irrigation with crop growth stages for maximum impact.
4. Implement Water Conservation Techniques
- Use mulch to retain soil moisture.
- Practice contour farming or terracing to reduce runoff in sloped areas.
5. Leverage Technology
- Install flow meters to monitor water usage.
- Use weather data and forecasting to plan irrigation schedules.
- Adopt precision agriculture tools to apply water more efficiently.
6. Regular System Maintenance
- Check for leaks, clogs, or wear in irrigation systems regularly.
- Calibrate systems to ensure even water distribution.
7. Crop Rotation and Selection
- Choose drought-resistant or low-water crops where appropriate.
- Rotate crops to maintain soil health and water efficiency.
8. Collect and Reuse Water
- Use rainwater harvesting systems.
- Implement tailwater recovery systems to recycle runoff water.
9. Train and Educate Workers
- Teach farmworkers about efficient irrigation techniques.
- Provide training on new technologies and sustainable practices.
10. Comply with Local Regulations
- Follow water use restrictions and conservation guidelines set by local authorities.
- Participate in programs promoting sustainable irrigation practices.
By integrating these practices, farmers can achieve better water resource management, reduce costs, and enhance agricultural productivity.